Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
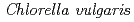 and nano zero-valent iron
and nano zero-valent ironIslam, M. S.*; Maamoun, I.; Falyouna, O.*; Eljamal, O.*; Saha, B. B.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 370, p.121005_1 - 121005_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:90.69(Chemistry, Physical)Arsenic waste must be carefully managed because of the adverse effects of arsenic in wastewater on the ecosystem. In the present study, an environmentally friendly novel composite of 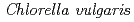 microalgae and nano-zero valent iron (NZVI) was employed as an adsorbent to eliminate arsenic from the aqueous environment. Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscope images were used to characterize and analyze the CV/NZVI composites. Batch tests using initial arsenic concentrations ranging from 5 to 100 mg/L were conducted to evaluate removal efficiencies. According to kinetic analysis, the best model for fitting the experimental data was the pseudo first-order model, which had the lowest Akaike information criterion (AIC), and Bayesian information criterion (BIC) values of -23.878 and -7.902, respectively. Results alluded that physisorption is the primary mechanism influenced by As-removal by CV/NZVI composite. Due to the negative sign of the enthalpy and Gibbs free energy, the thermodynamic investigation revealed that the adsorption reaction was exothermic and spontaneous. The thermodynamic analysis also affirmed that the arsenic removal process involved primarily physisorption and slight chemisorption phenomena. Meanwhile, 1.5 g/L CV/NZVI dosage achieved 99% As(V) removal efficiency in synthetic groundwater systems, confirming the high potential of the composite in complex aqueous systems.
microalgae and nano-zero valent iron (NZVI) was employed as an adsorbent to eliminate arsenic from the aqueous environment. Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscope images were used to characterize and analyze the CV/NZVI composites. Batch tests using initial arsenic concentrations ranging from 5 to 100 mg/L were conducted to evaluate removal efficiencies. According to kinetic analysis, the best model for fitting the experimental data was the pseudo first-order model, which had the lowest Akaike information criterion (AIC), and Bayesian information criterion (BIC) values of -23.878 and -7.902, respectively. Results alluded that physisorption is the primary mechanism influenced by As-removal by CV/NZVI composite. Due to the negative sign of the enthalpy and Gibbs free energy, the thermodynamic investigation revealed that the adsorption reaction was exothermic and spontaneous. The thermodynamic analysis also affirmed that the arsenic removal process involved primarily physisorption and slight chemisorption phenomena. Meanwhile, 1.5 g/L CV/NZVI dosage achieved 99% As(V) removal efficiency in synthetic groundwater systems, confirming the high potential of the composite in complex aqueous systems.
瀬古 典明; Basuki, F.*; 玉田 正男; 吉井 文男
Reactive and Functional Polymers, 59(3), p.235 - 241, 2004/07
被引用回数:52 パーセンタイル:82.06(Chemistry, Applied)近年、ヒ素の汚染による被害が世界各国で問題になっている。われわれは、ヒ素に対して選択性の高いジルコニウム基を放射線グラフト重合法により導入し、ヒ素除去吸着材を開発した。不織布基材にリン酸基を有するモノマーをグラフト反応させ、酸性下ジルコニウムを担持させた。ジルコニウム官能基量は吸着材1kgあたり4.1molであった。ヒ素の除去に関しては、従来のイオン交換樹脂等と比較すると、130倍もの速度で処理を行うことが可能にあり、総吸着容量も6倍程度の処理能力を有することがわかった。除去したヒ素は、水酸化ナトリウムを用いて回収することが知られているが、これまでは共存イオンの影響を受けていたものの、本吸着材では、その影響を受けず、処理速度も10倍以上で行うことが可能であった。広範囲のpHにおいてもその処理ができることを確認した。
坂東 昭次; H.HAMAGUCHI*; N.ONUMA*; Y.HIRAO*; H.YOKOYAMA*; M.FURUKAWA*
Geochem.Cosmochim.Acta, 33, p.507 - 518, 1969/00
被引用回数:34抄録なし
亀本 雄一郎; 山岸 滋
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 36(2), p.132 - 136, 1963/00
被引用回数:2抄録なし
Maamoun, I.; Falyouna, O.*; Shariful, I. M.*; Eljamal, R.*; Bensaida, K.*; 田中 万也; 徳永 紘平; Eljamal, O.*
no journal, ,
The main aim of this study is to investigate the potential of Mg(OH) coated iron nanoparticles in achieving improved arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. Set of batch tests has been conducted to understand the effect of several reaction factors, including coating ratio optimization, dosage, initial pH, temperature, and initial As(V) concentration. Results indicated that full coating was the optimal Mg(OH)
coated iron nanoparticles in achieving improved arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. Set of batch tests has been conducted to understand the effect of several reaction factors, including coating ratio optimization, dosage, initial pH, temperature, and initial As(V) concentration. Results indicated that full coating was the optimal Mg(OH) coating ratio which yielded full removal efficiency after 120 min reaction time, higher than that of nFe0 and Mg(OH)
coating ratio which yielded full removal efficiency after 120 min reaction time, higher than that of nFe0 and Mg(OH) coated iron nanoparticles with lower coating ratios. Furthermore, both strong acidic and high temperature conditions were favorable for inducing the arsenic removal performance of Mg(OH)
coated iron nanoparticles with lower coating ratios. Furthermore, both strong acidic and high temperature conditions were favorable for inducing the arsenic removal performance of Mg(OH) coated iron nanoparticles. Still, Mg(OH)
coated iron nanoparticles. Still, Mg(OH) coated iron nanoparticles could efficiently achieve comparable removal at a wide pH and temperature ranges. Such results implied the contribution of Mg(OH)
coated iron nanoparticles could efficiently achieve comparable removal at a wide pH and temperature ranges. Such results implied the contribution of Mg(OH) to As(V) removal via adsorption and the possible co-precipitation of As(III) with the released Mg
to As(V) removal via adsorption and the possible co-precipitation of As(III) with the released Mg from the coating shell dissolution. Besides, the progressive release of electrons from the iron core contributed to As(V) reduction to As(III). In conclusion, the proposed Mg(OH)
from the coating shell dissolution. Besides, the progressive release of electrons from the iron core contributed to As(V) reduction to As(III). In conclusion, the proposed Mg(OH) coated iron nanoparticles could be a perfect nanomaterial candidate for the real applications of arsenic removal from contaminated waters.
coated iron nanoparticles could be a perfect nanomaterial candidate for the real applications of arsenic removal from contaminated waters.